Table of Contents
Pointer in C Hancerrank Solution
In this Pointer in C Programming Tutorial at first we will learn about basic concepts of pointer after that we will see some pointer in c hackerrank solution for the practice of computer science students.
Frequently asked Questions
Some frequently asked questions from pointer in c programming are given below
- What is Pointer in C ?
- What is Call by Reference in C ?
- What is pointer to pointer in c ?
- Pointer in C hackerrank solution
What is Pointer in C ?
In C Programming a Pointer is variable which store the address of another variable.
Initialization of Pointer
Call By Reference in Pointer
#include<stdio.h>
void swap(int *x, int *y);
int main()
{
int m=22;
int n=44;
printf(“before swap m=%d and n=%d\n”,m,n);
swap(&m,&n);
printf(“after swap m=%d and n=%d\n”,m,n);
return 0;
}
void swap(int *x,int *y)
{
printf(“value of x=%u value of y =%u\n”,x,y);
printf(“before swap value stored at address x=%d and value stored at address y =%d\n”,*x,*y);
int temp;
temp=*x;
*x=*y;
*y=temp;
//s
printf(“value of x=%u value of y =%u\n”,x,y);
printf(“After swap value stored at address x=%d and value stored at address y =%d\n”,*x,*y);
}
Output
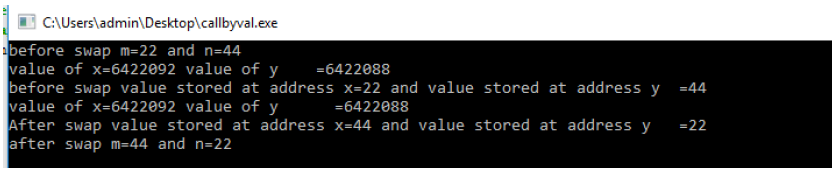
In the above program x and y are the memory address of m and n because in function calling address of m and n is passed.
Since x and y are the address so address remain same after swap but value stored at address x and address y will be swap.
Pointer to Pointer
We can also declare a pointer to pointer in C Programming. We can understand this using following program for pointer to pointer.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main ()
{
int a = 10;
int *p;
int **pp;
p = &a;
pp = &p;
printf(“address of a: %u\n”,p);
printf(“address of p: %u\n”,pp);
printf(“value stored at p: %d\n”,*p);
printf(“Value represented by double pointer %d\n”,**pp);
getch( );
}
output
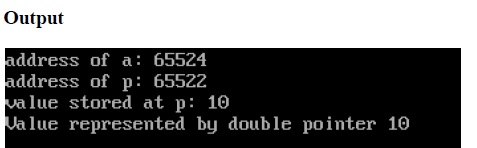
In the above Program pointer p is pointing to the address of a and pointer pp is a double pointer pointing to the address of pointer p.
In the next section we will discussed pointer in c hackerrank solution.
Pointer in C Hackerrank Solution
In this section we will understand the solution of problem on hackerrank based on pointer in c.
Problem
Complete the function void update(int *a,int *b). It receives two integer pointers, int* a and int* b. Set the value of a to their sum, b and to their absolute difference. There is no return value, and no return statement is needed.
a’ = a+b
b’ = |a-b|
Input Format
The input will contain two integers, a and b, separated by a newline.
Output Format
Modify the two values in place and the code stub main() will print their values.
Note: Input/ouput will be automatically handled. You only have to complete the function described in the ‘task’ section.
Sample Input
4
5
Sample Output
9
1
Explanation
a’ = 4 + 5 = 9
b’ = | 4 – 5 | = 1
Solution
Program to solve the above problem is given below
#include <stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void update(int *a,int *b) {
// Complete this function
int sum,diff;
sum = *a+*b;
diff = abs(*a-*b);
*a = sum;
*b = diff;
}
int main() {
int a, b;
int *pa = &a;
int *pb = &b;
clrscr();
scanf(“%d %d”, &a, &b);
update(pa, pb);
printf(“after update\n %d\n%d”, a, b);
getch();
return 0;
}
Output

For the above pointer in c hackerrank solution we use the following steps in the above program.
Step 1 – Included the required header files.
Step 2- Defined a function update( ) that takes two integer pointers, a and b, as arguments. We also declared two integer variables, ‘sum’ and ‘diff’. sum will store the sum of two integers, and diff will store the absolute difference.
Step 3 – Declared the main function. Inside main( ) function, we declared two integer variables, a and b, and two integer pointers, pa and pb, that point to a and b.
Step 4- We have used the scanf( ) function to read the inputs and called the update function to update the values of a and b.
Step 5– Display the result using printf( ) function.
Conclusion and Summary
In this C Tutorial of Pointer we have explained the basic concept of pointer. we have also explained the pointer in c hackerrank solution.
I hope this tutorial will be beneficial to students.


